How to open and read Excel files in C# and VB.NET
Excel remains a fundamental tool for data organization and analysis across numerous industries. However, efficiently managing diverse Excel formats can pose challenges for developers. GemBox.Spreadsheet provides a simple and intuitive API for opening and reading various Excel file formats like XLSX, XLS, XLSB, and ODS without using Microsoft Office Interop.
Many free tools like Open XML SDK can read some Excel file formats, but they are generally limited and can only display a low-level model of an Excel file. With GemBox.Spreadsheet you have a high-level model that supports reading, writing, modifying, and creating Excel files without studying the OpenXML specification. Apart from basic cell and worksheet operations it supports advanced features like charts, comments, pivot tables, formulas, shapes, and more.
In this article, you will learn how to use GemBox.Spreadsheet to open and read various Excel file formats in your C# and VB.NET applications.
You can navigate through the following sections:
- Using the GemBox.Spreadsheet free version
- How to open and read an Excel file in C# and VB.NET
- How to read a specific Excel sheet in C# and VB.NET
- How to read Excel cells using row and column index
- How to read Excel cells using cell name
- Supported file formats
Using the GemBox.Spreadsheet free version
Before you start, you need to install GemBox.Spreadsheet. The best way to do that is to install the NuGet Package by following these instructions:
- Add the GemBox.Spreadsheet package using the following command from the NuGet Package Manager Console:
Install-Package GemBox.Spreadsheet - After installing the package, you must call the ComponentInfo.SetLicense method before using any other member of the library.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
In this tutorial, by using "FREE-LIMITED-KEY", you will be using GemBox's free mode. This mode allows you to use the library without purchasing a license, but with some limitations. If you purchased a license, you can replace "FREE-LIMITED-KEY" with your serial key.
You can check our step-by-step guide for more information on how to install and set up GemBox.Spreadsheet.
How to open and read an Excel file in C# and VB.NET
The code below shows how you can open and read an XLSX (OpenXML) file using the GemBox.Spreadsheet .NET component.
using System;
using System.Text;
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
// Load the XLSX file.
var workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%");
var sb = new StringBuilder();
// Iterate through all worksheets in the XLSX file.
foreach (var worksheet in workbook.Worksheets)
{
sb.AppendLine();
sb.AppendFormat("{0} {1} {0}", new string('-', 30), worksheet.Name);
// Iterate through all rows in a worksheet.
foreach (var row in worksheet.Rows)
{
sb.AppendLine();
// Iterate through all allocated cells a row.
foreach (var cell in row.AllocatedCells)
{
if (cell.ValueType != CellValueType.Null)
{
var value = cell.Value.ToString();
if (value.Length > 15)
value = value.Remove(15) + "...";
sb.Append(string.Format("{0} [{1}]", value, cell.ValueType).PadRight(30));
}
else
sb.Append(new string(' ', 30));
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString());
}
}Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
' Load the XLSX file.
Dim workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%")
Dim sb = New StringBuilder()
' Iterate through all worksheets in the XLSX file.
For Each worksheet In workbook.Worksheets
sb.AppendLine()
sb.AppendFormat("{0} {1} {0}", New String("-"c, 30), worksheet.Name)
' Iterate through all rows in a worksheet.
For Each row In worksheet.Rows
sb.AppendLine()
' Iterate through all allocated cells in a row.
For Each cell In row.AllocatedCells
If cell.ValueType <> CellValueType.Null Then
Dim value = cell.Value.ToString()
If value.Length > 15 Then value = value.Remove(15) & "..."
sb.Append(String.Format("{0} [{1}]", value, cell.ValueType).PadRight(30))
Else
sb.Append(New String(" "c, 30))
End If
Next
Next
Next
Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString())
End Sub
End Module
The following screenshot shows all XLSX cell values read with GemBox.Spreadsheet.
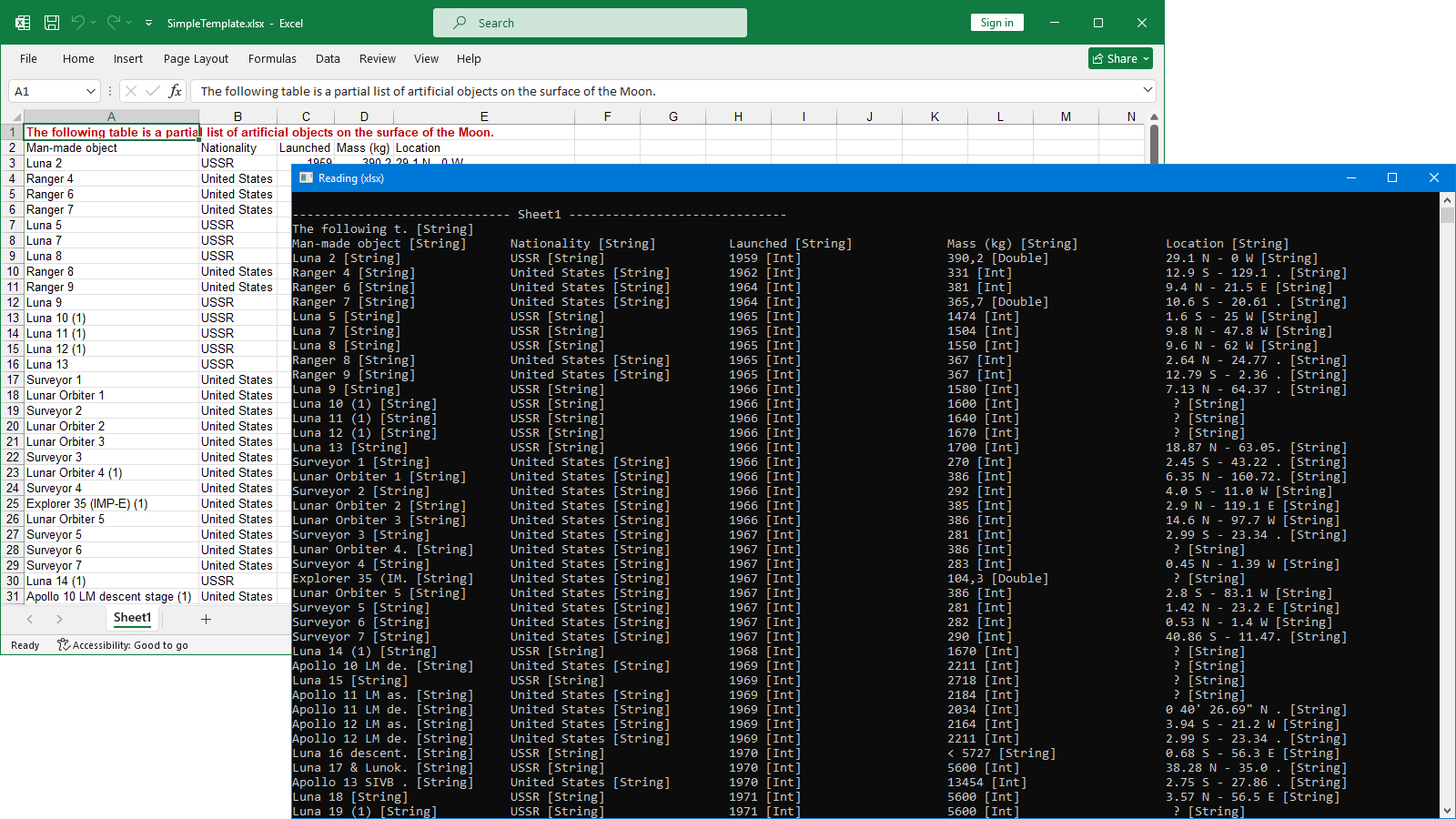
XLSX is the default format when creating a spreadsheet using modern versions of Excel. It was first introduced with Microsoft Office 2007 in the Office Open XML standard, a zipped, XML-based file format developed by Microsoft.
Since XLSX is, in essence, a set of zipped XML files, many free tools can read it, such as Open XML SDK. The main drawback of such tools is that they usually don't have a high-level model that supports reading, modifying, or creating files without studying OpenXML specifications. Also, they don't support other file formats or advanced features like formula calculation and data validation.
How to read a specific Excel sheet in C# and VB.NET
The code below demonstrates how you can use GemBox.Spreadsheet to read and extract data from a specific Excel sheet within an XLS file.
using System;
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
// Load the XLS file.
var workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%#CombinedTemplate.xls%");
// Get Excel worksheet by its name.
var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets["Moon Objects"];
// Check if the worksheet exists.
if (worksheet != null)
{
// Iterate through all rows in the worksheet.
foreach (ExcelRow row in worksheet.Rows)
{
// Iterate through all allocated cells in a row.
foreach (ExcelCell cell in row.AllocatedCells)
{
// Read cell's data.
string value = cell.Value?.ToString() ?? "EMPTY";
// For merged cells, read only the first cell's data.
if (cell.MergedRange != null && cell.MergedRange[0] != cell)
value = "MERGED";
// Display cell's value and type.
value = value.Length > 15 ? value.Remove(15) + "..." : value;
Console.Write($"{value} [{cell.ValueType}]".PadRight(30));
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}Imports System
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
' Load the XLS file.
Dim workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%#CombinedTemplate.xls%")
' Get Excel worksheet by its name.
Dim worksheet = workbook.Worksheets("Moon Objects")
' Check if the worksheet exists.
If worksheet IsNot Nothing Then
' Iterate through all rows in the worksheet.
For Each row As ExcelRow In worksheet.Rows
' Iterate through all allocated cells in a row.
For Each cell As ExcelCell In row.AllocatedCells
' Read cell's data.
Dim value As String = If(cell.Value?.ToString(), "EMPTY")
' For merged cells, read only the first cell's data.
If cell.MergedRange IsNot Nothing AndAlso cell.MergedRange(0) IsNot cell Then value = "MERGED"
' Display cell's value and type.
value = If(value.Length > 15, value.Remove(15) & "...", value)
Console.Write($"{value} [{cell.ValueType}]".PadRight(30))
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
End If
End Sub
End Module
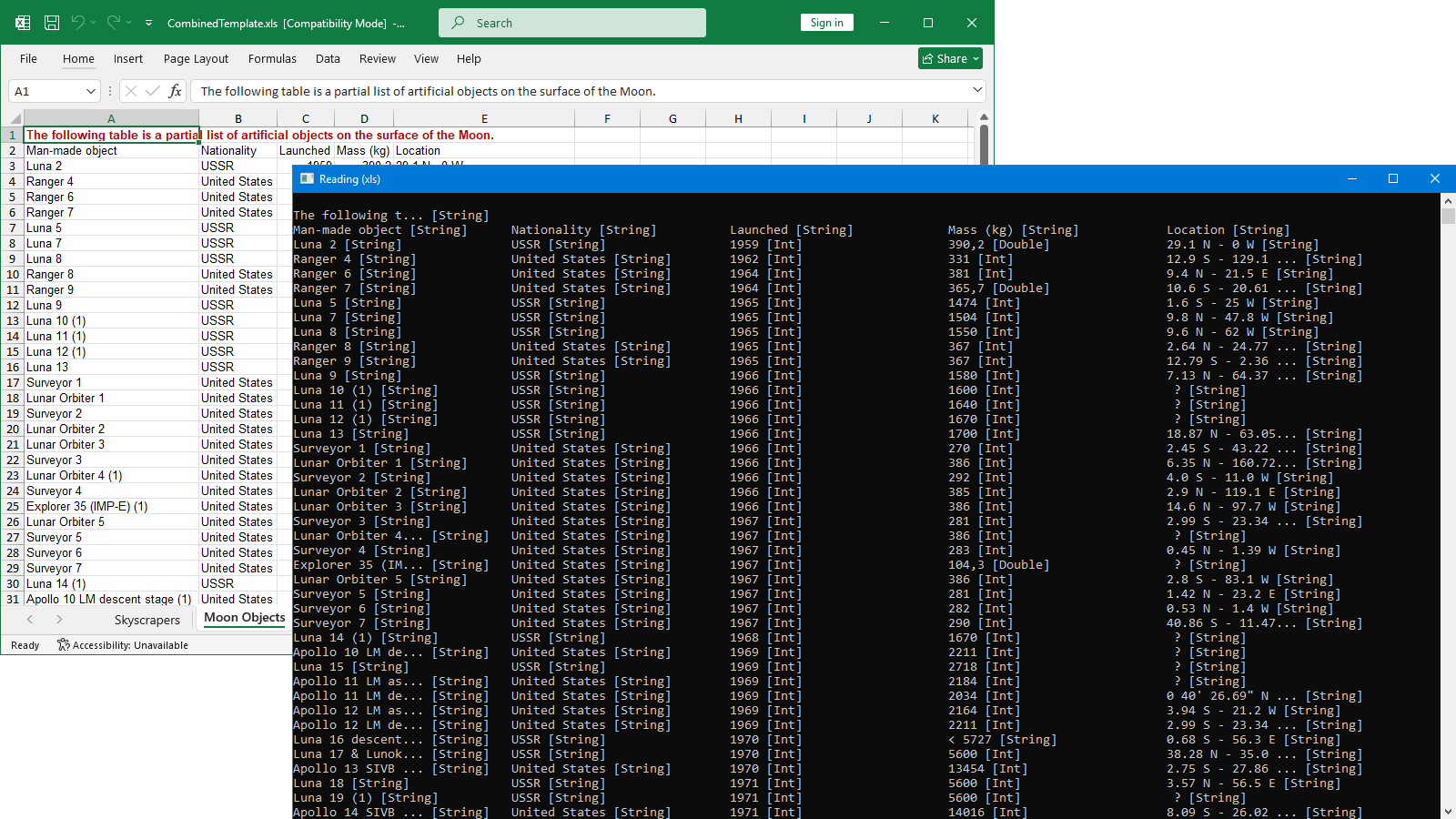
When you iterate through ExcelCell objects in an ExcelRow, you should use ExcelRow.AllocatedCells instead of ExcelRow.Cells to prevent unnecessary memory allocations.
You should also prefer iterating through cells in ExcelRow rather than ExcelColumn because cells are internally allocated in rows and not in columns.
How to read Excel cells using row and column index
The code below shows how to read cell information from an XLSB file using cell row and column index.
using System;
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
// Load the XLSB file.
var workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%");
// Iterate through all worksheets in the XLSB file.
foreach (ExcelWorksheet worksheet in workbook.Worksheets)
{
// Iterate through first 5 rows and columns.
for (int row = 0; row < 5; row++)
for (int column = 0; column < 5; column++)
{
// Get cell by the row and column index.
ExcelCell cell = worksheet.Cells[row, column];
// If cell is not empty, write its row index, column index, and value.
if (cell.ValueType != CellValueType.Null)
Console.WriteLine($"Cell [{cell.Row.Index}, {cell.Column.Index}]: {cell.Value}");
}
}
}
}Imports System
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
' Load the XLSB file.
Dim workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%")
' Iterate through all worksheets in the XLSB file.
For Each worksheet As ExcelWorksheet In workbook.Worksheets
' Iterate through first 5 rows and columns.
For row As Integer = 0 To 4
For column As Integer = 0 To 4
' Get cell by the row and column index.
Dim cell = worksheet.Cells(row, column)
' If cell is not empty, write its row index, column index, and value.
If cell.ValueType <> CellValueType.Null Then
Console.WriteLine($"Cell [{cell.Row.Index}, {cell.Column.Index}]: {cell.Value}")
End If
Next
Next
Next
End Sub
End Module
The following screenshot shows cell information extracted from an XLSB file using GemBox.Spreadsheet.
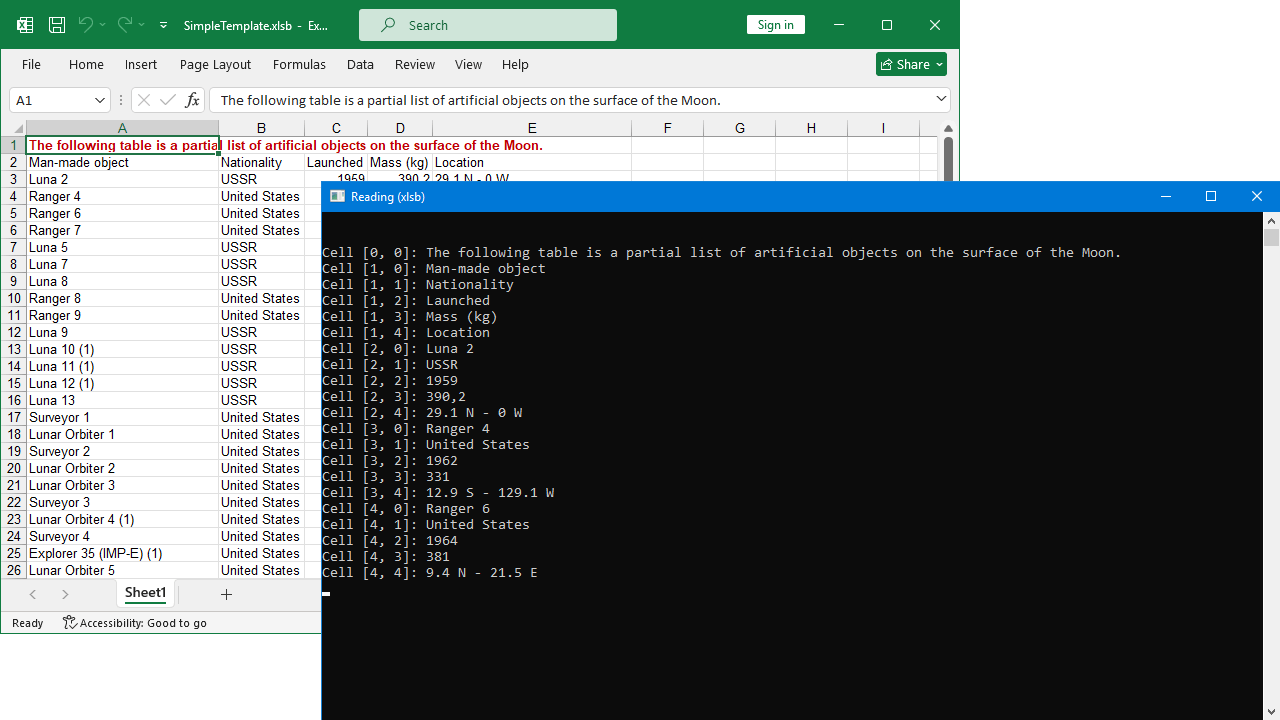
How to read Excel cells using cell name
The following code shows how to read a cell value from an ODS file using cell's name.
using System;
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
// Load the ODS file.
var workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%");
// Get the first worksheet.
var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get cell A1 and write its name and value.
var cell = worksheet.Cells["%CellName%"];
Console.WriteLine($"Cell {cell.Name}: {(cell.Value ?? "EMPTY")}");
}
}Imports System
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If you are using the Professional version, enter your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
' Load the ODS file.
Dim workbook As ExcelFile = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%")
' Get the first worksheet.
Dim worksheet As ExcelWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
' Get cell A1 and write its name and value.
Dim cell As ExcelCell = worksheet.Cells("%CellName%")
Console.WriteLine($"Cell {cell.Name}: {If(cell.Value, "EMPTY")}")
End Sub
End Module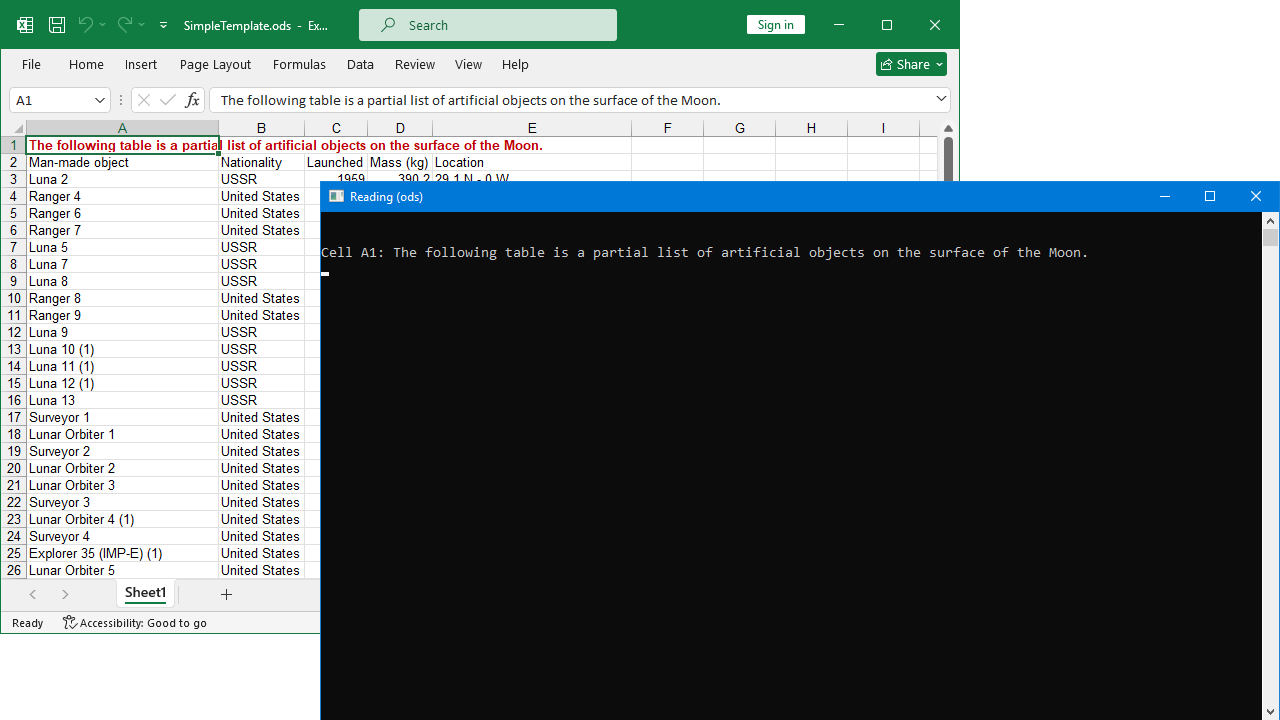
For more information on cell referencing, please check the Cell Referencing example.
Supported file formats
Microsoft Excel supports many file formats suited for spreadsheets, from old legacy file formats to the newest XML-based file formats. Microsoft Office Interop (Excel Automation) is a popular option for creating and reading Excel files from C# or VB.NET applications, but it has many drawbacks.
GemBox.Spreadsheet, as one of the best alternatives to Excel Automation, supports reading the following spreadsheet file formats using the same API: XLSX, XLS, XLSB, ODS, CSV, TXT, XLSM, XLTX, XLTM, XML, HTML, MHTML.
Conclusion
This article showed multiple ways you can open and read various Excel file formats in C# and VB.NET using the GemBox.Spreadsheet library.
For more information regarding the GemBox.Spreadsheet API, you can take a moment to read the documentation pages and browse through our examples with executable code sections.
If you have any questions regarding the examples, refer to our forum page or submit a ticket to our technical support.
