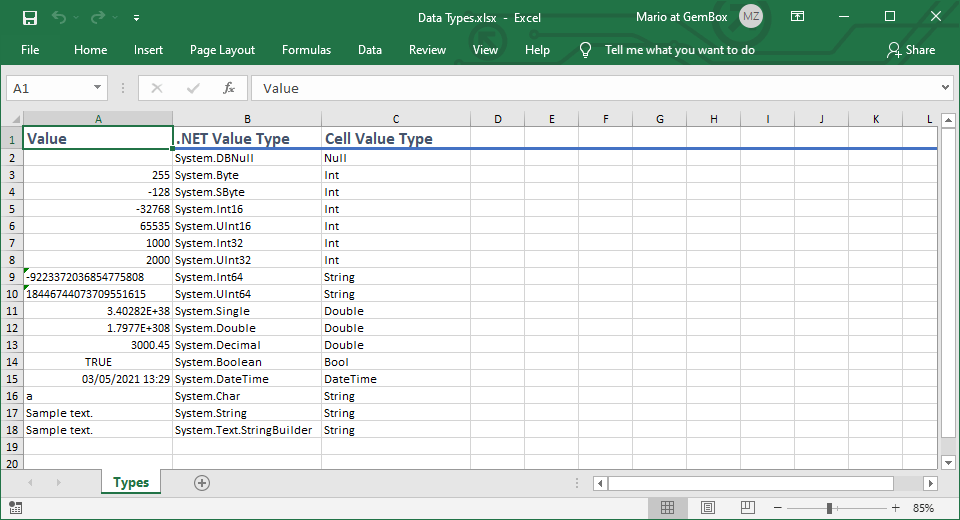
Merge and split (unmerge) Excel cells
The following example shows how to use GemBox.Spreadsheet to merge Excel cells and set the merged range's value and style with C# or VB.NET code.
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
var workbook = new ExcelFile();
var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1");
// Get the cell range.
var range = worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("B2:E5");
// Merge cells in the current range.
range.Merged = true;
// Set the value of the merged range.
range.Value = "Merged";
// Set the style of the merged range.
range.Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentStyle.Center;
// Set the style of the merged range using a cell within.
worksheet.Cells["C3"].Style.Borders
.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.All, SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Red), LineStyle.Double);
workbook.Save("Merged Cells.%OutputFileType%");
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook As New ExcelFile()
Dim worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
' Get the cell range.
Dim range = worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("B2:E5")
' Merge cells in the current range.
range.Merged = True
' Set the value of the merged range.
range.Value = "Merged"
' Set the style of the merged range.
range.Style.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignmentStyle.Center
' Set the style of the merged range using a cell within.
worksheet.Cells("C3").Style.Borders _
.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.All, SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Red), LineStyle.Double)
workbook.Save("Merged Cells.%OutputFileType%")
End Sub
End Module
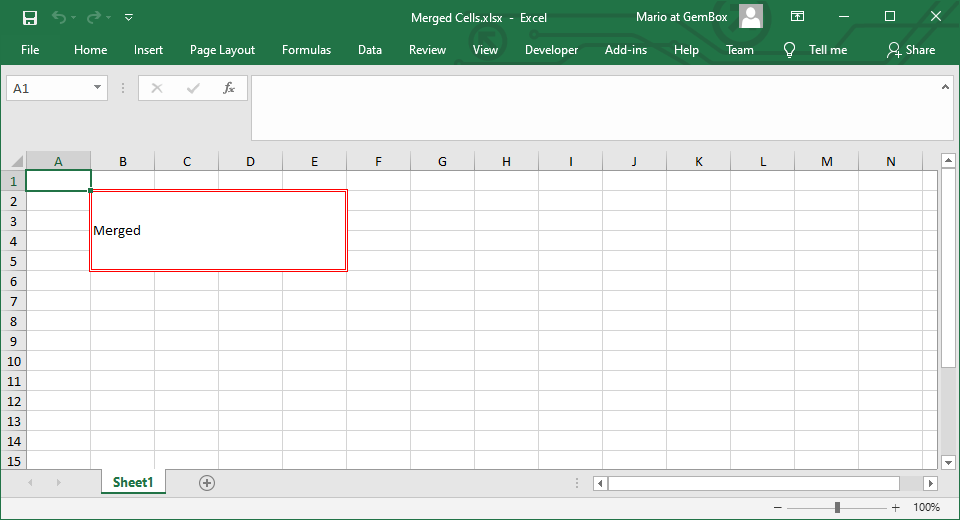
When merging a cell range, the top-left cell determines the value and style of the merged range, while the other cell data within the range is lost. This combines multiple cells into a larger cell, and any modifications to the value or style of any cell in the range will affect the entire merged range.
How to unmerge Excel cells
The following example shows how you can find the first merged range in a sheet and split (unmerge) those Excel cells by setting the CellRange.Merged property to false.
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
using System.Linq;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
var workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%");
var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Get the first merged range.
var mergedRange = worksheet.Rows
.SelectMany(row => row.AllocatedCells)
.Select(cell => cell.MergedRange)
.FirstOrDefault(range => range != null);
if (mergedRange != null)
{
// Important, you cannot unmerge the ExcelCell.MergedRange property.
// In other words, the following is not allowed: mergedRange.Merged = false;
// Instead, you need to retrieve the same CellRange from the ExcelWorksheet and then unmerge it.
// This kind of implementation was chosen for performance reasons.
worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange(mergedRange.Name).Merged = false;
worksheet.Cells[mergedRange.StartPosition].Value = "Unmerged";
}
workbook.Save("Unmerged Cells.xlsx");
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Imports System.Linq
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%")
Dim worksheet = workbook.Worksheets(0)
' Get the first merged range.
Dim mergedRange = worksheet.Rows _
.SelectMany(Function(row) row.AllocatedCells) _
.Select(Function(cell) cell.MergedRange) _
.FirstOrDefault(Function(range) range IsNot Nothing)
If mergedRange <> Nothing Then
' Important, you cannot unmerge the ExcelCell.MergedRange property.
' In other words, the following is not allowed: mergedRange.Merged = False
' Instead, you need to retrieve the same CellRange from the ExcelWorksheet and then unmerge it.
' This kind of implementation was chosen for performance reasons.
worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange(mergedRange.Name).Merged = False
worksheet.Cells(mergedRange.StartPosition).Value = "Unmerged"
End If
workbook.Save("Unmerged Cells.xlsx")
End Sub
End Module
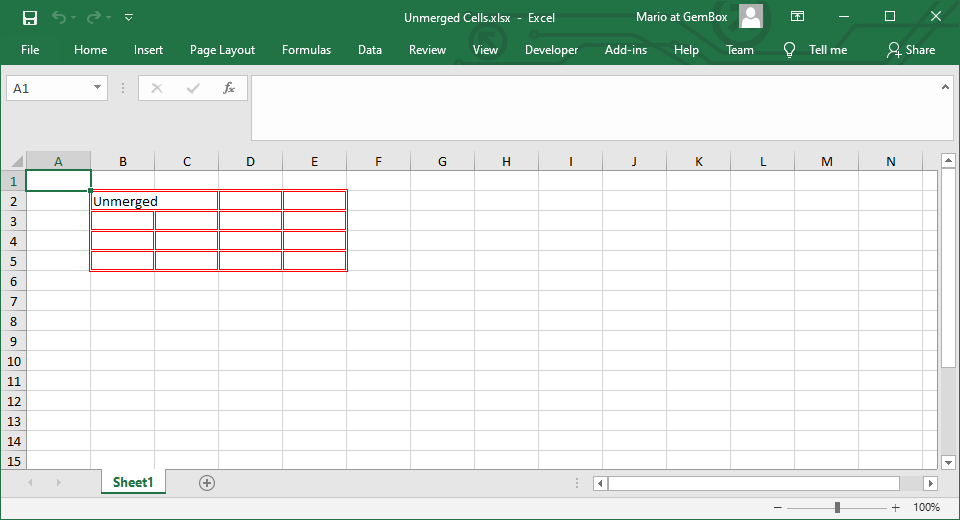
When you split a cell range, only the value of the top-left cell will remain. The rest of the cells in that range will be empty. Also, all cells will have the same style that's taken from the previous merged range. If you want to remove the style from an ExcelCell object, you can use the Clear method with the ClearOptions.Format argument.