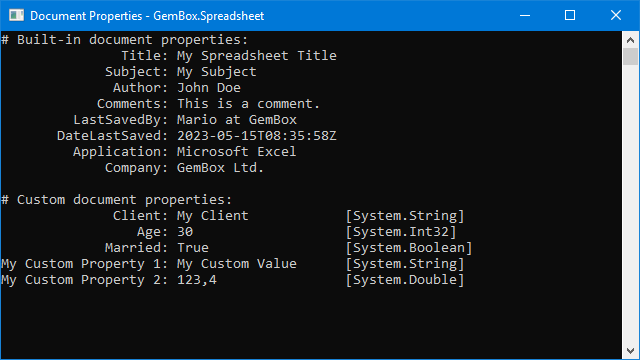
Manage Excel Document Properties
The following example shows how to read and write built-in and custom Excel document properties (Excel file metadata) using GemBox.Spreadsheet in C# and VB.NET.
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
var workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%");
var properties = workbook.DocumentProperties;
Console.WriteLine("# Built-in document properties:");
// Write built-in document properties.
properties.BuiltIn[BuiltInDocumentProperties.Title] = "My Spreadsheet Title";
properties.BuiltIn[BuiltInDocumentProperties.DateLastSaved] = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ");
// Read built-in document properties.
foreach (var builtinProperty in properties.BuiltIn)
Console.WriteLine($"{builtinProperty.Key,20}: {builtinProperty.Value}");
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("# Custom document properties:");
// Write custom document properties.
properties.Custom["My Custom Property 1"] = "My Custom Value";
properties.Custom["My Custom Property 2"] = 123.4;
// Read custom document properties.
foreach (var customProperty in properties.Custom)
Console.WriteLine($"{customProperty.Key,20}: {customProperty.Value,-20} [{customProperty.Value.GetType()}]");
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Imports System
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%InputFileName%")
Dim properties = workbook.DocumentProperties
Console.WriteLine("# Built-in document properties:")
' Write built-in document properties.
properties.BuiltIn(BuiltInDocumentProperties.Title) = "My Spreadsheet Title"
properties.BuiltIn(BuiltInDocumentProperties.DateLastSaved) = DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ")
' Read built-in document properties.
For Each builtinProperty In properties.BuiltIn
Console.WriteLine($"{builtinProperty.Key,20}: {builtinProperty.Value}")
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Console.WriteLine("# Custom document properties:")
' Write custom document properties.
properties.Custom("My Custom Property 1") = "My Custom Value"
properties.Custom("My Custom Property 2") = 123.4
' Read custom document properties.
For Each customProperty In properties.Custom
Console.WriteLine($"{customProperty.Key,20}: {customProperty.Value,-20} [{customProperty.Value.GetType()}]")
Next
End Sub
End Module
For more information about the document properties API, refer to our documentation page.
To learn how to view or change properties for an Office file using Microsoft Office applications, check this article.