Create Named Ranges in Excel
The following example shows how to create and retrieve defined names or named ranges in an Excel file from C# and VB.NET applications, using the GemBox.Spreadsheet library.
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
var workbook = new ExcelFile();
var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Names");
// Create a defined name for a constant value with a global scope.
workbook.DefinedNames.AddDefinedName("Tax", "0.2", -1);
// Retrieve defined name.
DefinedName taxConstant = workbook.DefinedNames["Tax"];
// Use defined name with formula.
worksheet.Cells["A1"].Value = taxConstant.Name;
worksheet.Cells["B1"].Formula = "=Tax";
worksheet.Cells["B1"].Style.NumberFormat = "0%";
// Create a named range for cell "A3" with a local scope.
worksheet.Cells["A2"].Value = "Price";
worksheet.Cells["A3"].Value = 240;
worksheet.Cells["A4"].Value = 180;
worksheet.Cells["A5"].Value = 210;
worksheet.NamedRanges.Add("Prices", worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("A3"));
// Retrieve named range.
NamedRange priceRange = worksheet.NamedRanges["Prices"];
// Modify named range's cell reference to cells "A3:A5".
priceRange.Range = worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("A3:A5");
// Use named range with formulas.
worksheet.Cells["B2"].Value = "Total";
worksheet.Cells["B3"].Formula = "=Prices * (Tax + 1)";
worksheet.Cells["B4"].Formula = "=Prices * (Tax + 1)";
worksheet.Cells["B5"].Formula = "=Prices * (Tax + 1)";
workbook.Save("Defined Names.%OutputFileType%");
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook As New ExcelFile()
Dim worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Names")
' Create a defined name for a constant value with a global scope.
workbook.DefinedNames.AddDefinedName("Tax", "0.2", -1)
' Retrieve defined name.
Dim taxConstant As DefinedName = workbook.DefinedNames("Tax")
' Use defined name with formula.
worksheet.Cells("A1").Value = taxConstant.Name
worksheet.Cells("B1").Formula = "=Tax"
worksheet.Cells("B1").Style.NumberFormat = "0%"
' Create a named range for cell "A3" with a local scope.
worksheet.Cells("A2").Value = "Price"
worksheet.Cells("A3").Value = 240
worksheet.Cells("A4").Value = 180
worksheet.Cells("A5").Value = 210
worksheet.NamedRanges.Add("Prices", worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("A3"))
' Retrieve named range.
Dim priceRange As NamedRange = worksheet.NamedRanges("Prices")
' Modify named range's cell reference to cells "A3:A5".
priceRange.Range = worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("A3:A5")
' Use named range with formulas.
worksheet.Cells("B2").Value = "Total"
worksheet.Cells("B3").Formula = "=Prices * (Tax + 1)"
worksheet.Cells("B4").Formula = "=Prices * (Tax + 1)"
worksheet.Cells("B5").Formula = "=Prices * (Tax + 1)"
workbook.Save("Defined Names.%OutputFileType%")
End Sub
End Module
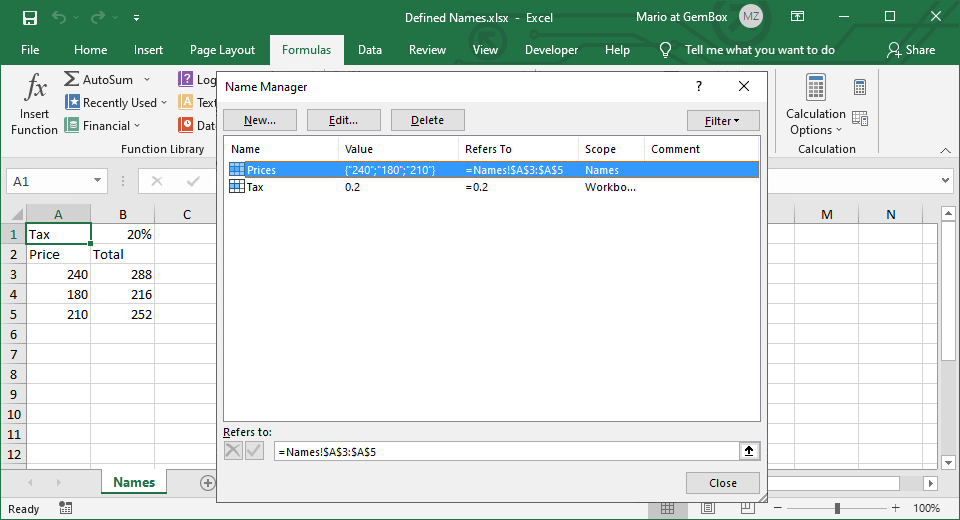
Defined names are used as user-friendly references to single cells, cell ranges, constant values, or formulas. These descriptive names enable you to specify cell references without relying on columns and rows, thereby enhancing the readability of your workbook.
With GemBox.Spreadsheets you can access defined names via ExcelWorkbook.DefinedNames and ExcelWorksheet.NamedRanges properties. The difference is that NamedRanges is a collection of NamedRange objects, filtered DefinedName objects that reference cells in a global scope (ExcelWorkbook) or a local scope (ExcelWorksheet).