Getting started with GemBox.Spreadsheet
GemBox.Spreadsheet is a .NET component that enables you to read, write, convert, and print spreadsheet files (XLSX, XLS, XLSB, CSV, HTML, and ODS) from .NET applications. GemBox.Spreadsheet requires only .NET. It supports a wide range of .NET versions, as listed below: Before you can use GemBox.Spreadsheet, you need to install it in your project. The best way is by adding a GemBox.Spreadsheet NuGet package via NuGet Package Manager in Visual Studio. To install the package, you can follow the steps listed below. However, please note that this guide assumes you have already set up a Visual Studio project. If you haven't done that yet, you can refer to the official tutorial for guidance. As an alternative, you can open the NuGet Package Manager Console (Tools -> NuGet Package Manager -> Package Manager Console) and run the following command: We also provide DLL and setup files on GemBox.Spreadsheet's Downloads page. A link for the latest setup file is located at the bottom of the page, under the 'Global Assembly' section. Once you have installed GemBox.Spreadsheet, all you have to do is add the using directive and make sure you call the The SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense requires a license key as a parameter. If you are using the component in a Free mode, use "FREE-LIMITED-KEY" as a license key, and if you have purchased a Professional license, use the key you got in your email after the purchase. You can read more about GemBox.Spreadsheet's working modes on the Evaluation and Licensing page. After that, you can write your application code for working with spreadsheets, like the code below. It shows how to create a simple Excel workbook using GemBox.Spreadsheet's content model, add an You can click the 'Run Example' button to run the code and download the resulting file. You can also change the output format by selecting a corresponding file type from the 'Output file type' dropdown control.Requirements
Installation
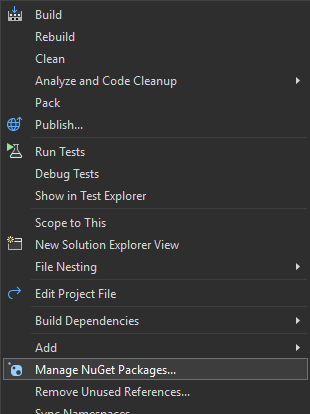
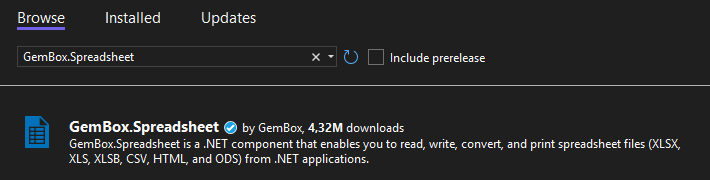
Install-Package GemBox.SpreadsheetUsage
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense method before using any member of the component. We suggest putting the call at the beginning of the Main() method.ExcelWorksheet, populate cells using ExcelCell, and then save the ExcelFile to an XLSX file.
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
ExcelFile workbook = new ExcelFile();
ExcelWorksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1");
ExcelCell cell = worksheet.Cells["A1"];
cell.Value = "Hello World!";
workbook.Save("HelloWorld.%OutputFileType%");
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook As New ExcelFile()
Dim worksheet As ExcelWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
Dim cell As ExcelCell = worksheet.Cells("A1")
cell.Value = "Hello World!"
workbook.Save("HelloWorld.%OutputFileType%")
End Sub
End Module
To learn more about GemBox.Spreadsheet, check out our collection of examples listed on the menu. These examples will show you how to use the component in various spreadsheet-processing tasks and platforms. Additionally, for detailed information on the API, head to our documentation pages. This resource offers a comprehensive API reference, explaining each method and property available within the component. CLI coding agents such as GitHub Copilot, Claude Code, and OpenAI Codex can write valid GemBox code when enabled with our gembox-skill.AI Coding