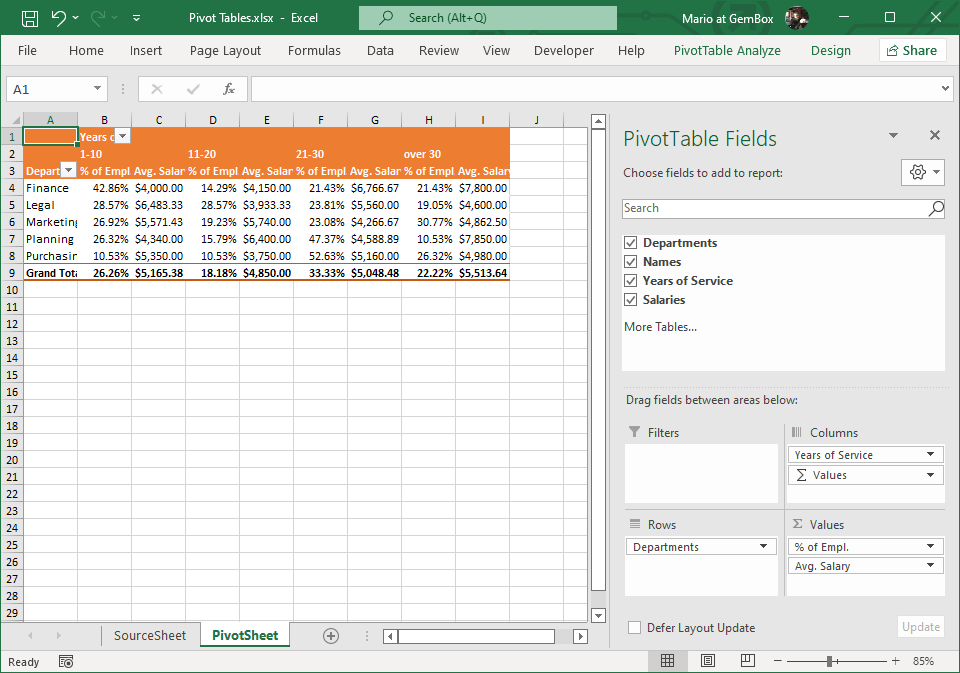
Create Excel Pivot Tables
The following example shows how you can use GemBox.Spreadsheet to create a Pivot Table from a range of cells in an Excel file and customize its appearance, with C# and VB.NET.
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
using GemBox.Spreadsheet.PivotTables;
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
var workbook = new ExcelFile();
var worksheet1 = workbook.Worksheets.Add("SourceSheet");
// Specify sheet formatting.
worksheet1.Rows[0].Style.Font.Weight = ExcelFont.BoldWeight;
worksheet1.Columns[0].SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter);
worksheet1.Columns[1].SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter);
worksheet1.Columns[2].SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter);
worksheet1.Columns[3].SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter);
worksheet1.Columns[3].Style.NumberFormat = "[$$-409]#,##0.00";
var cells = worksheet1.Cells;
// Specify header row.
cells[0, 0].Value = "Departments";
cells[0, 1].Value = "Names";
cells[0, 2].Value = "Years of Service";
cells[0, 3].Value = "Salaries";
// Insert random data to sheet.
var random = new Random();
var departments = new string[] { "Legal", "Marketing", "Finance", "Planning", "Purchasing" };
var names = new string[] { "John Doe", "Fred Nurk", "Hans Meier", "Ivan Horvat" };
var years = new string[] { "1-10", "11-20", "21-30", "over 30" };
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
cells[i + 1, 0].Value = departments[random.Next(departments.Length)];
cells[i + 1, 1].Value = names[random.Next(names.Length)] + ' ' + (i + 1).ToString();
cells[i + 1, 2].Value = years[random.Next(years.Length)];
cells[i + 1, 3].SetValue(random.Next(10, 101) * 100);
}
// Create pivot cache from cell range "SourceSheet!A1:D100".
var cache = workbook.PivotCaches.AddWorksheetSource("SourceSheet!A1:D100");
// Create new sheet for pivot table.
var worksheet2 = workbook.Worksheets.Add("PivotSheet");
// Create pivot table "Company Profile" using the specified pivot cache and add it to the worksheet at the cell location 'A1'.
var table = worksheet2.PivotTables.Add(cache, "Company Profile", "A1");
// Aggregate 'Names' values into count value and show it as a percentage of row.
var field = table.DataFields.Add("Names");
field.Function = PivotFieldCalculationType.Count;
field.ShowDataAs = PivotFieldDisplayFormat.PercentageOfRow;
field.Name = "% of Empl.";
// Aggregate 'Salaries' values into average value.
field = table.DataFields.Add("Salaries");
field.Function = PivotFieldCalculationType.Average;
field.Name = "Avg. Salary";
field.NumberFormat = "[$$-409]#,##0.00";
// Group rows into 'Departments'.
table.RowFields.Add("Departments");
// Group columns first into 'Years of Service' and then into 'Values' (count 'Names' and average 'Salaries').
table.ColumnFields.Add("Years of Service");
table.ColumnFields.Add(table.DataPivotField);
// Specify the string to be displayed in row and column header.
table.RowHeaderCaption = "Departments";
table.ColumnHeaderCaption = "Years of Service";
// Do not show grand totals for rows.
table.RowGrandTotals = false;
// Set pivot table style.
table.BuiltInStyle = BuiltInPivotStyleName.PivotStyleMedium10;
workbook.Save("Pivot Tables.xlsx");
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet.PivotTables
Imports System
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook As New ExcelFile()
Dim worksheet1 = workbook.Worksheets.Add("SourceSheet")
' Specify sheet formatting.
worksheet1.Rows(0).Style.Font.Weight = ExcelFont.BoldWeight
worksheet1.Columns(0).SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter)
worksheet1.Columns(1).SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter)
worksheet1.Columns(2).SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter)
worksheet1.Columns(3).SetWidth(3, LengthUnit.Centimeter)
worksheet1.Columns(3).Style.NumberFormat = "[$$-409]#,##0.00"
Dim cells = worksheet1.Cells
' Specify header row.
cells(0, 0).Value = "Departments"
cells(0, 1).Value = "Names"
cells(0, 2).Value = "Years of Service"
cells(0, 3).Value = "Salaries"
' Insert random data to sheet.
Dim random As New Random()
Dim departments = New String() {"Legal", "Marketing", "Finance", "Planning", "Purchasing"}
Dim names = New String() {"John Doe", "Fred Nurk", "Hans Meier", "Ivan Horvat"}
Dim years = New String() {"1-10", "11-20", "21-30", "over 30"}
For i As Integer = 0 To 100
cells(i + 1, 0).Value = departments(random.Next(departments.Length))
cells(i + 1, 1).Value = names(random.Next(names.Length)) + " "c + (i + 1).ToString()
cells(i + 1, 2).Value = years(random.Next(years.Length))
cells(i + 1, 3).SetValue(random.Next(10, 101) * 100)
Next
' Create pivot cache from cell range "SourceSheet!A1:D100".
Dim cache = workbook.PivotCaches.AddWorksheetSource("SourceSheet!A1:D100")
' Create new sheet for pivot table.
Dim worksheet2 = workbook.Worksheets.Add("PivotSheet")
' Create pivot table "Company Profile" using the specified pivot cache and add it to the worksheet at the cell location 'A1'.
Dim table = worksheet2.PivotTables.Add(cache, "Company Profile", "A1")
' Aggregate 'Names' values into count value and show it as a percentage of row.
Dim field = table.DataFields.Add("Names")
field.Function = PivotFieldCalculationType.Count
field.ShowDataAs = PivotFieldDisplayFormat.PercentageOfRow
field.Name = "% of Empl."
' Aggregate 'Salaries' values into average value.
field = table.DataFields.Add("Salaries")
field.Function = PivotFieldCalculationType.Average
field.Name = "Avg. Salary"
field.NumberFormat = "[$$-409]#,##0.00"
' Group rows into 'Departments'.
table.RowFields.Add("Departments")
' Group columns first into 'Years of Service' and then into 'Values' (count 'Names' and average 'Salaries').
table.ColumnFields.Add("Years of Service")
table.ColumnFields.Add(table.DataPivotField)
' Specify the string to be displayed in row and column header.
table.RowHeaderCaption = "Departments"
table.ColumnHeaderCaption = "Years of Service"
' Do not show grand totals for rows.
table.RowGrandTotals = False
' Set pivot table style.
table.BuiltInStyle = BuiltInPivotStyleName.PivotStyleMedium10
workbook.Save("Pivot Tables.xlsx")
End Sub
End Module
Note that pivot Tables are supported in XLSX file format only. This next example shows how to update the source data and calculate the pivot table using the As shown in the code, to calculate the pivot table call the Note that while the calculated values will be included in all output formats, pivot table styles and formatting are currently only supported in XLSX format.Pivot table calculation
PivotTable.Calculate method.using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
using GemBox.Spreadsheet.PivotTables;
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
var workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%#PivotTableSource.xlsx%");
var sourceSheet = workbook.Worksheets["SourceSheet"];
var pivotSheet = workbook.Worksheets["PivotSheet"];
var pivotTable = pivotSheet.PivotTables[0];
// Calculate the pivot table with existing values in the pivot cache.
pivotTable.Calculate();
Console.WriteLine("Pivot table values before:");
foreach (var row in pivotSheet.Rows)
{
foreach (var cell in row.AllocatedCells)
Console.Write(cell.GetFormattedValue().PadRight(30));
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Change the values in the source sheet.
sourceSheet.Cells["D2"].Value = 15300;
sourceSheet.Cells["D4"].Value = 13300;
sourceSheet.Cells["D7"].Value = 18500;
// Refresh the pivot cache.
pivotTable.PivotCache.Refresh();
// Calculate the pivot table.
pivotTable.Calculate();
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("Pivot table values after:");
foreach (var row in pivotSheet.Rows)
{
foreach (var cell in row.AllocatedCells)
Console.Write(cell.GetFormattedValue().PadRight(30));
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet.PivotTables
Imports System
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook = ExcelFile.Load("%#PivotTableSource.xlsx%")
Dim sourceSheet = workbook.Worksheets("SourceSheet")
Dim pivotSheet = workbook.Worksheets("PivotSheet")
Dim pivotTable = pivotSheet.PivotTables(0)
' Calculate the pivot table with existing values in the pivot cache.
pivotTable.Calculate()
Console.WriteLine("Pivot table values before:")
For Each row In pivotSheet.Rows
For Each cell In row.AllocatedCells
Console.Write(cell.GetFormattedValue().PadRight(30))
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
' Change the values in the source sheet.
sourceSheet.Cells("D2").Value = 15300
sourceSheet.Cells("D4").Value = 13300
sourceSheet.Cells("D7").Value = 18500
' Refresh the pivot cache.
pivotTable.PivotCache.Refresh()
' Calculate the pivot table.
pivotTable.Calculate()
Console.WriteLine("-------------------------------------")
Console.WriteLine("Pivot table values after:")
For Each row In pivotSheet.Rows
For Each cell In row.AllocatedCells
Console.Write(cell.GetFormattedValue().PadRight(30))
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
End Sub
End Module
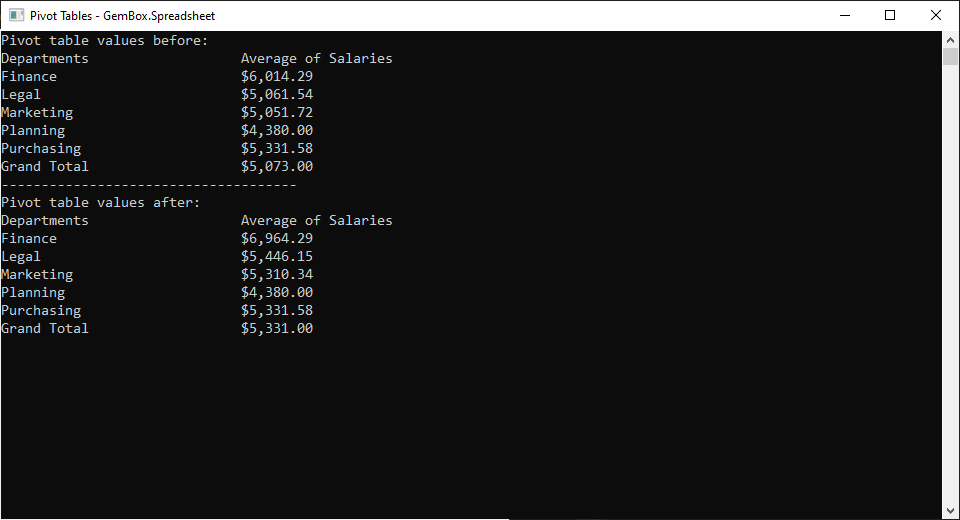
PivotTable.Calculate method which will update the related cells in the worksheet. Since the calculation uses values stored in the PivotCache you need to make sure to call the PivotCache.Refresh() method after changing cell values referenced by the table.