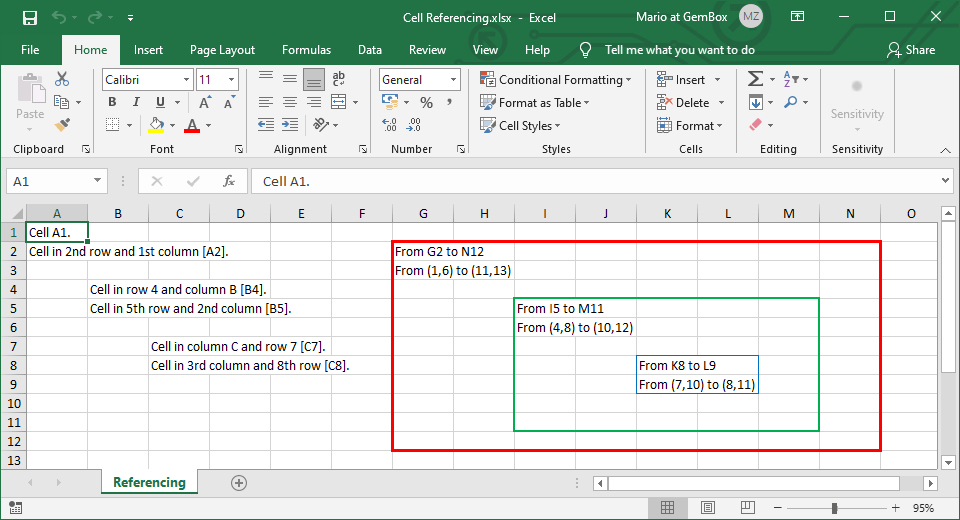
Referencing Excel cell and range
The following example shows various techniques for referencing cells (ExcelCell) and cell ranges (CellRange) in C# and VB.NET with GemBox.Spreadsheet.
using GemBox.Spreadsheet;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
var workbook = new ExcelFile();
var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Referencing");
// Referencing cells from sheet using cell names and indexes.
worksheet.Cells["A1"].Value = "Cell A1.";
worksheet.Cells[1, 0].Value = "Cell in 2nd row and 1st column [A2].";
// Referencing cells from row using cell names and indexes.
worksheet.Rows["4"].Cells["B"].Value = "Cell in row 4 and column B [B4].";
worksheet.Rows[4].Cells[1].Value = "Cell in 5th row and 2nd column [B5].";
// Referencing cells from column using cell names and indexes.
worksheet.Columns["C"].Cells["7"].Value = "Cell in column C and row 7 [C7].";
worksheet.Columns[2].Cells[7].Value = "Cell in 3rd column and 8th row [C8].";
// Referencing cell range using A1 notation [G2:N12].
var range = worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("G2:N12");
range[0].Value = $"From {range.StartPosition} to {range.EndPosition}";
range[1, 0].Value = $"From ({range.FirstRowIndex},{range.FirstColumnIndex}) to ({range.LastRowIndex},{range.LastColumnIndex})";
range.Style.Borders.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.Outside,
SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Red),
LineStyle.Thick);
// Referencing cell range using absolute position [I5:M11].
range = range.GetSubrangeAbsolute(4, 8, 10, 12);
range[0].Value = $"From {range.StartPosition} to {range.EndPosition}";
range[1, 0].Value = $"From ({range.FirstRowIndex},{range.FirstColumnIndex}) to ({range.LastRowIndex},{range.LastColumnIndex})";
range.Style.Borders.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.Outside,
SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Green),
LineStyle.Medium);
// Referencing cell range using relative position [K8:L10].
range = range.GetSubrangeRelative(3, 2, 2, 2);
range[0].Value = $"From {range.StartPosition} to {range.EndPosition}";
range[1, 0].Value = $"From ({range.FirstRowIndex},{range.FirstColumnIndex}) to ({range.LastRowIndex},{range.LastColumnIndex})";
range.Style.Borders.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.Outside,
SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Blue),
LineStyle.Thin);
workbook.Save("Cell Referencing.%OutputFileType%");
}
}
Imports GemBox.Spreadsheet
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
SpreadsheetInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Dim workbook As New ExcelFile()
Dim worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add("Referencing")
' Referencing cells from sheet using cell names and indexes.
worksheet.Cells("A1").Value = "Cell A1."
worksheet.Cells(1, 0).Value = "Cell in 2nd row and 1st column [A2]."
' Referencing cells from row using cell names and indexes.
worksheet.Rows("4").Cells("B").Value = "Cell in row 4 and column B [B4]."
worksheet.Rows(4).Cells(1).Value = "Cell in 5th row and 2nd column [B5]."
' Referencing cells from column using cell names and indexes.
worksheet.Columns("C").Cells("7").Value = "Cell in column C and row 7 [C7]."
worksheet.Columns(2).Cells(7).Value = "Cell in 3rd column and 8th row [C8]."
' Referencing cell range using A1 notation [G2:N12].
Dim range = worksheet.Cells.GetSubrange("G2:N12")
range(0).Value = $"From {range.StartPosition} to {range.EndPosition}"
range(1, 0).Value = $"From ({range.FirstRowIndex},{range.FirstColumnIndex}) to ({range.LastRowIndex},{range.LastColumnIndex})"
range.Style.Borders.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.Outside,
SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Red),
LineStyle.Thick)
' Referencing cell range using absolute position [I5:M11].
range = range.GetSubrangeAbsolute(4, 8, 10, 12)
range(0).Value = $"From {range.StartPosition} to {range.EndPosition}"
range(1, 0).Value = $"From ({range.FirstRowIndex},{range.FirstColumnIndex}) to ({range.LastRowIndex},{range.LastColumnIndex})"
range.Style.Borders.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.Outside,
SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Green),
LineStyle.Medium)
' Referencing cell range using relative position [K8:L10].
range = range.GetSubrangeRelative(3, 2, 2, 2)
range(0).Value = $"From {range.StartPosition} to {range.EndPosition}"
range(1, 0).Value = $"From ({range.FirstRowIndex},{range.FirstColumnIndex}) to ({range.LastRowIndex},{range.LastColumnIndex})"
range.Style.Borders.SetBorders(MultipleBorders.Outside,
SpreadsheetColor.FromName(ColorName.Blue),
LineStyle.Thin)
workbook.Save("Cell Referencing.%OutputFileType%")
End Sub
End Module
GemBox.Spreadsheet supports referencing Excel cells or range of cells using either names or zero-based indexes.
If using names, specify the position of cells with column letters and row numbers in an A1 notation and select the required cell reference using CellRange.GetSubrange methods.
When using indexes, specify the absolute or relative position of cells and select the required cell reference using the CellRange.GetSubrangeAbsolute or CellRange.GetSubrangeRelative method.
The following is the list of some A1 notations supported by GemBox.Spreadsheet that can be used to retrieve a cell range with an A1-style reference:
| Cell Reference | Description |
|---|---|
| A1 | Range that includes a single cell A1. |
| A1:C3 | Range that includes cells from the top-left cell A1 to the bottom-right cell C3. |
| A:A | Range that includes the entire column A. |
| A:C | Range that includes the entire columns from A to C. |
| 1:1 | Range that includes the entire row 1. |
| 1:3 | Range that includes the entire rows from 1 to 3. |
Additionally, there are two special cell range references that you can retrieve with the following:
- The
ExcelWorksheet.GetUsedCellRangemethod for selecting a range of allocated cells in the worksheet. - The
CellRange.GetCurrentRegionmethod for getting a region to which the cell range belongs to.
Once you reference an Excel cell range, you can iterate and read or write their values through its cells. Check the Reading and Writing examples for more information about fast and efficient cell iteration.
You can also merge or style and format cells within the cell range, or you can execute actions like calculating, filtering, and sorting cells. You can also use cell range when configuring objects like Charts and Pivot Tables data sources.