Load and Save Progress Reporting and Cancellation
The following example demonstrates how to output the save progress of a large Word file to the console, using the GemBox.Document component.
using GemBox.Document;
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
Console.WriteLine("Creating document");
// Create large document.
var document = new DocumentModel();
var section = new Section(document);
document.Sections.Add(section);
for (var i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
section.Blocks.Add(new Paragraph(document, i.ToString()));
// Create save options.
var saveOptions = new DocxSaveOptions();
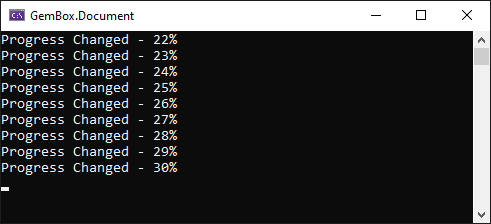
saveOptions.ProgressChanged += (eventSender, args) =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"Progress changed - {args.ProgressPercentage}%");
};
// Save document.
document.Save("document.docx", saveOptions);
}
}
Imports GemBox.Document
Imports System
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
Console.WriteLine("Creating document")
' Create large document.
Dim document As New DocumentModel()
Dim section As New Section(document)
document.Sections.Add(section)
For i As Integer = 0 To 10000
section.Blocks.Add(New Paragraph(document, i.ToString()))
Next
' Create save options.
Dim saveOptions = New DocxSaveOptions()
AddHandler saveOptions.ProgressChanged,
Sub(eventSender, args)
Console.WriteLine($"Progress changed - {args.ProgressPercentage}%")
End Sub
' Save document.
document.Save("document.docx", saveOptions)
End Sub
End Module
The operations that support progress reporting and canceling are loading of DOCX files and saving of DOCX, PDF, and image files.
As you can see you can track the operations by handling the The following example shows how to use Tasks in a WPF application to run the load operation on a new thread and how to use the The ProgressChanged event is fired on the same thread that started the operation. Therefore, if the operation starts in the UI thread of a WPF application, the thread will be blocked. Because of that, the application won't show the changes made as a response to the fired event. Similarly to WPF, to show the progress of an operation in the UI, it is necessary to run the process on a separate thread and report the changes on the UI thread. The following example shows how to do that in a Windows Forms application. The following example shows how to cancel the saving of a document in a console application after a specific time. The example below shows how to implement a button in WPF that cancels the load operation.DocxLoadOptions.ProgressChanged, DocxSaveOptions.ProgressChanged, PdfSaveOptions.ProgressChanged, and ImageSaveOptions.ProgressChanged events.Progress reporting in WPF
SynchronizationContext to make changes to the progress bar on the UI thread.<Window x:Class="MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Progress reporting in WPF" Height="150" Width="300">
<Grid>
<ProgressBar HorizontalAlignment="Left" Height="32" Margin="27,73,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="200" Name="progressBar"/>
<Button x:Name="button" Content="Load" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="27,19,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="236" Height="36" Click="loadButton_Click"/>
<Label x:Name="percentageLabel" Content="" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="239,77,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" RenderTransformOrigin="0.867,0.59"/>
</Grid>
</Window>using GemBox.Document;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
InitializeComponent();
}
private async void loadButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Capture the current context on the UI thread.
var context = SynchronizationContext.Current;
// Create load options.
var loadOptions = new DocxLoadOptions();
loadOptions.ProgressChanged += (eventSender, args) =>
{
var percentage = args.ProgressPercentage;
// Invoke on the UI thread.
context.Post(progressPercentage =>
{
// Update UI.
this.progressBar.Value = (int)progressPercentage;
this.percentageLabel.Content = progressPercentage.ToString() + "%";
}, percentage);
};
this.percentageLabel.Content = "0%";
// Use tasks to run the load operation in a new thread.
var file = await Task.Run(() => DocumentModel.Load("%#LargeDocument.docx%", loadOptions));
}
}
Imports GemBox.Document
Imports System.Threading
Imports System.Threading.Tasks
Imports System.Windows
Class MainWindow
Public Sub New()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Async Sub loadButton_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs)
' Capture the current context on the UI thread.
Dim context = SynchronizationContext.Current
' Create load options.
Dim loadOptions = New DocxLoadOptions()
AddHandler loadOptions.ProgressChanged,
Sub(eventSender, args)
Dim percentage = args.ProgressPercentage
' Invoke on the UI thread.
context.Post(
Sub(progressPercentage)
' Update UI.
Me.progressBar.Value = CType(progressPercentage, Integer)
Me.percentageLabel.Content = progressPercentage.ToString() & "%"
End Sub, percentage)
End Sub
Me.percentageLabel.Content = "0%"
' Use tasks to run the load operation in a new thread.
Await Task.Run(
Sub()
DocumentModel.Load("%#LargeDocument.docx%", loadOptions)
End Sub)
End Sub
End Class
Progress reporting in Windows Forms
using GemBox.Document;
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public partial class MainForm : Form
{
public MainForm()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
InitializeComponent();
}
private async void loadButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Capture the current context on the UI thread.
var context = SynchronizationContext.Current;
// Create load options.
var loadOptions = new DocxLoadOptions();
loadOptions.ProgressChanged += (eventSender, args) =>
{
var percentage = args.ProgressPercentage;
// Invoke on the UI thread.
context.Post(progressPercentage =>
{
// Update UI.
this.progressBar.Value = (int)progressPercentage;
this.percentageLabel.Text = progressPercentage.ToString() + "%";
}, percentage);
};
this.percentageLabel.Text = "0%";
// Use tasks to run the load operation in a new thread.
var file = await Task.Run(() => DocumentModel.Load("%#LargeDocument.docx%", loadOptions));
}
}
Imports GemBox.Document
Imports System
Imports System.Threading
Imports System.Threading.Tasks
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Public Class MainForm
Public Sub New()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Async Sub LoadButton_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles LoadButton.Click
' Capture the current context on the UI thread.
Dim context = SynchronizationContext.Current
' Create load options.
Dim loadOptions = New DocxLoadOptions()
AddHandler loadOptions.ProgressChanged,
Sub(eventSender, args)
Dim percentage = args.ProgressPercentage
' Invoke on the UI thread.
context.Post(
Sub(progressPercentage)
' Update UI.
Me.ProgressBar.Value = CType(progressPercentage, Integer)
Me.PercentageLabel.Text = progressPercentage.ToString() & "%"
End Sub, percentage)
End Sub
Me.PercentageLabel.Text = "0%"
' Use tasks to run the load operation in a new thread.
Await Task.Run(
Sub()
DocumentModel.Load("%#LargeDocument.docx%", loadOptions)
End Sub)
End Sub
End Class
Cancellation
using GemBox.Document;
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
// Create document.
var document = new DocumentModel();
var section = new Section(document);
document.Sections.Add(section);
for (var i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
section.Blocks.Add(new Paragraph(document, i.ToString()));
var stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
// Create save options.
var saveOptions = new DocxSaveOptions();
saveOptions.ProgressChanged += (sender, args) =>
{
// Cancel operation after five seconds.
if (stopwatch.Elapsed.Seconds >= 5)
args.CancelOperation();
};
try
{
document.Save("Cancellation.docx", saveOptions);
Console.WriteLine("Operation fully finished");
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Operation was cancelled");
}
}
}
Imports GemBox.Document
Imports System
Imports System.Diagnostics
Module Program
Sub Main()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
' Create document.
Dim document As New DocumentModel()
Dim section As New Section(document)
document.Sections.Add(section)
For i As Integer = 0 To 10000
section.Blocks.Add(New Paragraph(document, i.ToString()))
Next
Dim stopwatch = New Stopwatch()
stopwatch.Start()
' Create save options.
Dim saveOptions = New DocxSaveOptions()
AddHandler saveOptions.ProgressChanged,
Sub(eventSender, args)
' Cancel operation after five seconds.
If stopwatch.Elapsed.Seconds >= 5 Then
args.CancelOperation()
End If
End Sub
Try
document.Save("Cancellation.docx", saveOptions)
Console.WriteLine("Operation fully finished")
Catch ex As OperationCanceledException
Console.WriteLine("Operation was cancelled")
End Try
End Sub
End Module
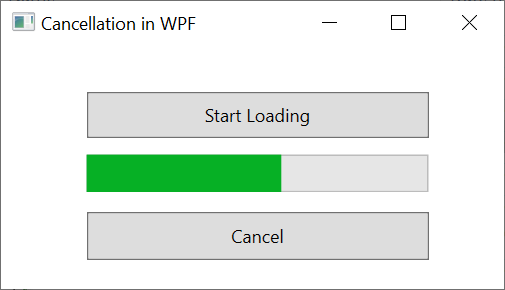
Cancellation in WPF
<Window x:Class="MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="Cancellation in WPF" Height="200" Width="350">
<Grid>
<Button x:Name="loadButton" Content="Start Loading" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="57,31,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="228" Height="31" Click="loadButton_Click" />
<Button x:Name="cancelButton" Content="Cancel" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="57,111,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="228" Height="32" Click="cancelButton_Click" />
<ProgressBar HorizontalAlignment="Left" Height="25" Margin="57,73,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="228" Name="progressBar" />
</Grid>
</Window>using GemBox.Document;
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
private volatile bool cancellationRequested;
public MainWindow()
{
// If using the Professional version, put your serial key below
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY");
InitializeComponent();
}
private async void loadButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Capture the current context on the UI thread.
var context = SynchronizationContext.Current;
var loadOptions = new DocxLoadOptions();
loadOptions.ProgressChanged += (eventSender, args) =>
{
// Show progress.
context.Post(progressPercentage => this.progressBar.Value = (int)progressPercentage, args.ProgressPercentage);
// Cancel if requested.
if (this.cancellationRequested)
args.CancelOperation();
};
try
{
var file = await Task.Run(() => DocumentModel.Load("%#LargeDocument.docx%", loadOptions));
}
catch (OperationCanceledException)
{
// Operation cancelled.
}
}
private void cancelButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
this.cancellationRequested = true;
}
}
Imports GemBox.Document
Imports System
Imports System.Threading
Imports System.Threading.Tasks
Imports System.Windows
Class MainWindow
Private Property cancellationRequested As Boolean
Public Sub New()
' If using the Professional version, put your serial key below.
ComponentInfo.SetLicense("FREE-LIMITED-KEY")
InitializeComponent()
End Sub
Private Async Sub loadButton_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs) Handles loadButton.Click
' Capture the current context on the UI thread.
Dim context = SynchronizationContext.Current
' Create load options.
Dim loadOptions = New DocxLoadOptions()
AddHandler loadOptions.ProgressChanged,
Sub(eventSender, args)
' Show progress.
context.Post(
Sub(progressPercentage)
Me.progressBar.Value = CType(progressPercentage, Integer)
End Sub, args.ProgressPercentage)
' Cancel if requested.
If Me.cancellationRequested Then
args.CancelOperation()
End If
End Sub
Try
Dim file = Await Threading.Tasks.Task.Run(
Function() As DocumentModel
Return DocumentModel.Load("%#LargeDocument.docx%", loadOptions)
End Function)
Catch ex As OperationCanceledException
' Operation cancelled.
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub cancelButton_Click(sender As Object, e As RoutedEventArgs) Handles cancelButton.Click
Me.cancellationRequested = True
End Sub
End Class